For millions of patients worldwide, the simple act of moving has become a huge task. Due to injury, illness, or advancing age, impaired physical mobility presents complex challenges for patients and healthcare providers. Nurses come up with impaired mobility care plans and nursing diagnosis to ease the burden and to make the healing process smooth.
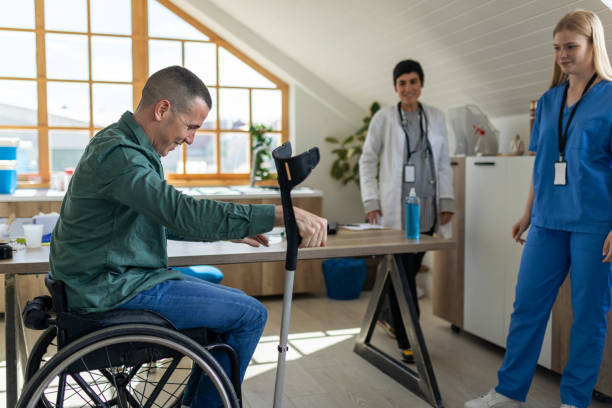

Nursing diagnosis for impaired physical mobility requires a multidisciplinary approach, integrating physical therapy, occupational therapy, and patient education. These are included in the impaired physical mobility care plan. This article will act as a guide into the deeper intricacies of the care plan and explore how nurses work to keep patients moving, engaged, and on the path to recovery.
READ ALSO: Ultimate guide for nursing care plan: Explained types, samples, and templates
What is an impaired physical mobility nursing diagnosis?
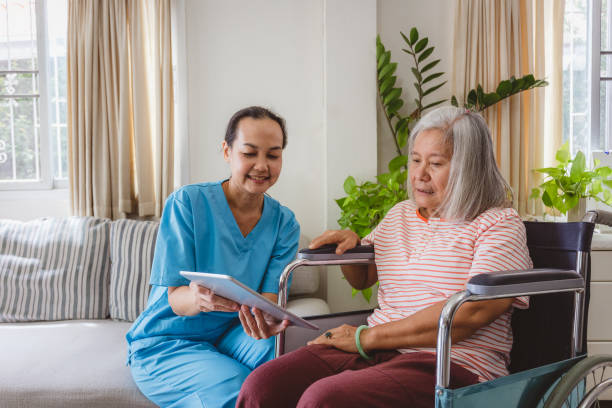

The nursing diagnosis of impaired physical mobility is a clinical assessment made by a nurse about a patient’s reduced capability to move without assistance or engage in physical tasks due to different factors. This diagnosis is based on a comprehensive evaluation of subjective and objective information, including the patient’s complaints of pain, uncoordinated movements, dependence on aid, and restricted movements.
Even if the patient’s primary issue is impaired physical mobility, the nurses investigate the underlying causes to ensure the condition is treated to its root. The diagnosis helps create a care plan tailored to the specific patient’s condition to enhance their mobility, and overall health, and avoid complications.
READ ALSO: Constipation nursing care plans and diagnosis
Main causes
Physical impaired mobility can arise as a result of many factors, including:
- Neurological disorders like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, or multiple sclerosis
- Chronic pain syndromes that limit movement
- Musculoskeletal conditions such as arthritis, muscle weakness, or fractures
- Cardiovascular issues leading to reduced endurance and shortness of breath
- Prolonged immobilization or bed rest, leads to muscle atrophy
- Obesity, which can strain joints or soft tissues
- Injuries or trauma affecting bones, joints, or soft tissues
- Psychological factors like fear of falling or depression
- Age-related changes in balance, strength, and coordination
- Side effects of certain medications that cause weakness or dizziness.
Factors related to mobility across the lifespan
Factors related to mobility across the lifespan include:
Infancy and early childhood
- Development Milestones: crawling, standing walking.
- Congenital conditions: cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy.
- Injury and trauma: caused by falls and small accidents which are common in small children.
Childhood and Adolescence
- Growth spurts: rapid growth can temporarily affect coordination, making adolescents more prone to injuries.
- Sports and physical activity: injuries are common among children.
- Genetic conditions: juvenile arthritis and scoliosis may develop at this time
Adulthood
- Lifestyle factors: factors like whether one exercise or the type of occupation can indicate whether one will experience impaired physical mobility.
- Chronic conditions: diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases can reduce overall stamina and mobility.
- Injuries and accidents: injuries are also common in adulthood due to falls. Sometimes the accidents can leave the patients immobile because of spinal cord injuries.
Older adulthood:
- Age-related changes: as we grow old, our muscle mass and strength tend to decrease and our joints become stiff due to wear and tear. This affects mobility and balance
- Chronic Conditions: some chronic conditions associated with old age include osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and Parkinson’s disease. These diseases mainly affect movement and coordination.
- Falls and balance issues: balance problems can significantly limit an older adult’s ability to move independently, making them prone to falls.
Major signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of impaired physical mobility are categorized into subjective and objective data-based, based on reports from patients and the nurse’s assessment.
Subjective data (patient reports)
- Refusal to move
- Expressing physical discomfort and pain while moving
Objective data (nurse assessments)
- Poor balance
- Postal inability
- Gait disturbances
- Contractures
- Limited range of motion
- Diminished muscle strength
- Uncoordinated movements
Effects of immobility
The effects of impaired physical mobility can be profound. These effects can impact nearly every system in the body. Some major effects include:
- Joint contractions
- Bone demineralization
- Reduced cardiac output
- Decreased lung expansion
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Low self-esteem
- Low confidence
Expected outcomes/ nursing goals
After the impaired physical mobility care plan is implemented, the expected outcomes are:
- The patient will engage in their daily activities and adhere to prescribed therapies.
- The patient should show progress in their physical mobility by being able to move from bed to wheelchair independently.
- The patient should be capable of performing prescribed exercises aimed at improving physical mobility.
- The patient assesses the level of discomfort and the effectiveness of treatment.
Nursing assessment related to impaired physical mobility
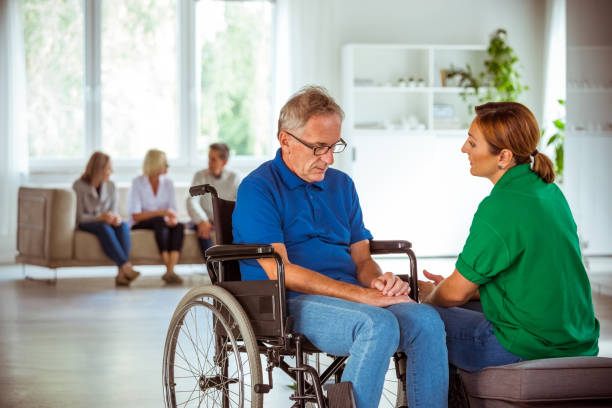

The initial stage of nursing care involves conducting a nursing assessment, where the nurse will collect physical, psychosocial, emotional, and diagnostic information. The nursing assessment involves:
- Asses for conditions that cause impaired mobility.
- Note the prescribed movement limitations.
- Assess for discomfort and restricted range of movement.
- Evaluate strength and range of movement.
- Exercise nursing discretion before initiating mobility.
- Assess the need for multidisciplinary care.
- Evaluate equipment needs.
- Note any signs of disinterest or reluctance.
- Assess whether there is an appropriate environment and support in place for the patient.
READ ALSO: NR 599 Week 2 Discussion Pre TANIC Self-Assessment and Reflection Post
Nursing interventions for impaired physical mobility
Nursing interventions and care play a crucial role in the patient’s recovery. They include:
- Encourage the patient to engage in activities to the best of their ability.
- Administer medication to alleviate pain.
- Plan activities to coincide with periods of rest to prevent overwhelming the patient.
- Supply adaptive tools that facilitate optimal mobility based on the patient’s capabilities.
- Administer a passive range of motion exercises if the patient cannot perform them independently.
- Advocate for proper nutrition and hydration.
- Engage the patient’s family and caregivers to foster their commitment to the patient’s well-being.
- Collaborate with the multidisciplinary team to guide exercises.
- Organize continued support upon discharge.
- Establish realistic goals, such as assisting the patient to sit up in bed.
- Offer positive affirmation to reinforce progress.
Nursing care plans for impaired physical mobility care plan
Nursing care plans are beneficial for organizing assessments and interventions to address short and long-term care goals for patients with impaired physical mobility. Here is an example:
Diagnostic statement
Impaired physical mobility related to general weakness and dizziness as a result of medications.
Expected outcomes
- Improved strength and energy levels.
- Reduced dizziness
- Increased activity tolerance
Assessment
- Vital signs monitoring
Vital signs monitoring like blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration rate will check for any underlying conditions.
- Musculoskeletal assessment
Assessing muscle strength and joint function will help asses for any stiffness or pain that might contribute to weakness.
Impaired physical mobility interventions
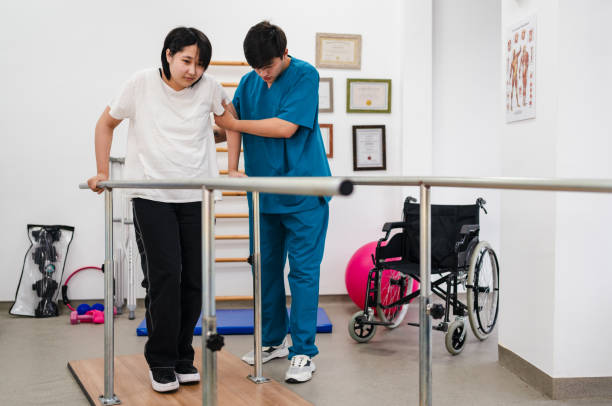

Medication management:
Review and adjust the patient’s dosage to reduce the impact on the patient’s daily activities.
Physical therapy and exercise
Develop a tailored exercise program that will enhance stability, improve muscle endurance, and reduce the risk of falls.
Patient education
Educate the patient about the potential side effects of their medications and fall prevention techniques.
FAQS for impaired physical mobility care plan
What are impaired physical mobility nursing care plans? Impaired physical mobility nursing plans are the nursing assessments, diagnoses, interventions, and goals of people with impaired physical mobility.
What are nursing priorities for clients with impaired physical mobility? Nursing priorities for clients with impaired physical mobility are:
- Handling patient safety.
- Educating and training patients on their medications and assistive devices.
- Preventing falls and injuries.
What are nursing care plan goals & expected outcomes for impaired physical mobility? Some expected outcomes for impaired physical mobility include the patient showing measures to increase mobility, performing physical activities independently, and learning how to use adaptive devices to boost mobility.
Impaired physical mobility is a significant challenge that affects millions worldwide, disrupting their daily activities. However, with a well-crafted impaired physical mobility care plan, the patient is empowered to regain mobility and as a result, independence. Each care plan is tailored for specific patients to ensure each goal is attained. Nurses play an important role in restoring movement and enhancing health.
References
https://nurseslabs.com/impaired-physical-mobility
https://www.carepatron.com/templates/impaired-physical-mobility-nursing-care-plan
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK591828
https://elsevier.health/en-US/preview/mobility-impairment-cpg